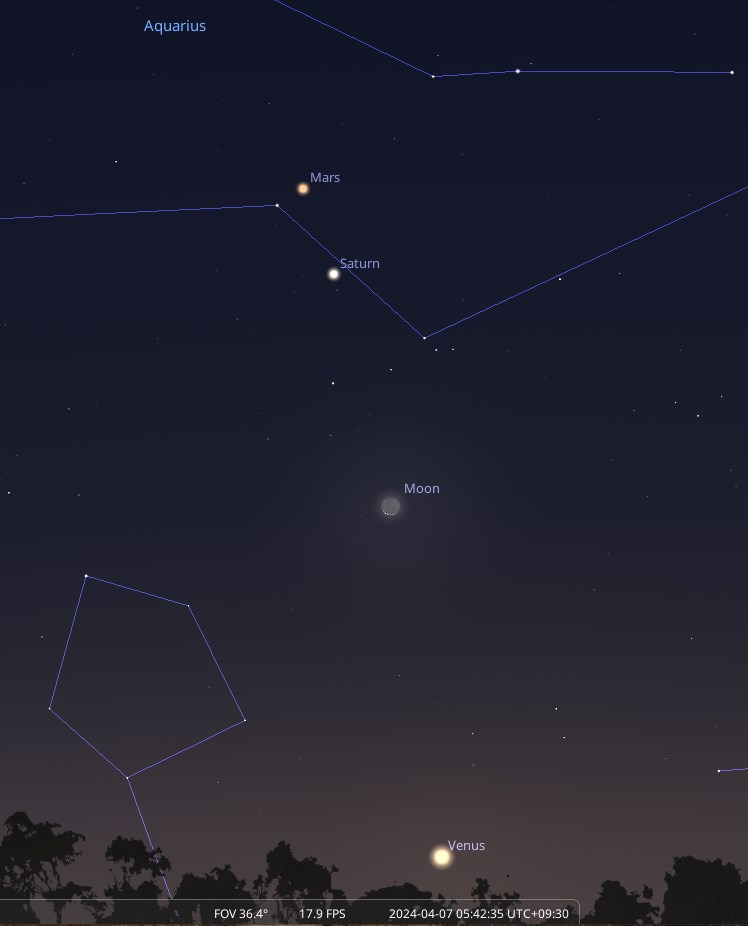
A guide to what's up in the sky for Southern Australia
Starwatch for February 2026 - Mon 2nd Feb 2026
Published 2nd Feb 2026
During these warm February evenings, the summer Milky Way is visible directly overhead, running north-south across the sky. The evening sky is resplendent with many brilliant stars. From Capella in the north to the Pointers in the south, the sky is a sheer delight to explore.
NGC 2439—Open Star Cluster - Sun 1st Feb 2026
Published 1st Feb 2026
NGC 2439—Open Star Cluster - Distance: 12,500 light years
Starwatch for January 2026 - Tue 30th Dec 2025
Published 30th Dec 2025
We can think of our location in the universe along the lines of an address. The street would be planet Earth, the local government area would be the solar system, and the country would be the Milky Way Galaxy.
M1 - the Crab Nebula - Mon 29th Dec 2025
Published 29th Dec 2025
Distance: 6,500 light years
Starwatch for December 2025 - Tue 25th Nov 2025
Published 25th Nov 2025
All the stars we see in the night sky belong to our Milky Way galaxy. However, there are some objects outside of the Milky Way galaxy that can be seen quite clearly with no or little optical power.
Starwatch for November 2025 - Wed 29th Oct 2025
Published 29th Oct 2025
A 101 years ago, on November 23, 1924, the universe got larger.
Starwatch for October 2025 - Thu 2nd Oct 2025
Published 2nd Oct 2025
Astronomical distances can be mind boggling. Our closest neighbour, the Moon, is 380,000 kms away — equal to about 10 trips around Earth’s equator.
Starwatch for September 2025 - Wed 3rd Sep 2025
Published 3rd Sep 2025
A few lingering stars of winter are still in view during the evening. Antares, Altair, Vega have lit up the cold winter nights for us. But there is really only one bright star that puts in its best showing during these early spring nights:
NGC 7293 – The Helix Nebula - Tue 2nd Sep 2025
Published 2nd Sep 2025
Image © Patrick Cosgrove. The Helix Nebula, also known as NGC 7293, is a planetary nebula (PN) located in the constellation Aquarius.
Starwatch for August 2025 - Sun 3rd Aug 2025
Published 3rd Aug 2025
Imagine yourself sitting on a rock on the dark side of Moon, gazing up at the Milky Way. There's no stray lights, no atmosphere to dull your view of the night sky. The stars are so brilliant, so big, you could reach out and touch them.
NGC 4755 - Fri 1st Aug 2025
Published 1st Aug 2025
The Jewel Box Star Cluster. Image © Sergio Equivar, Buenos Aires, Argentina
Starwatch for July 2025 - Thu 3rd Jul 2025
Published 3rd Jul 2025
Look up overhead on any of these frosty winter’s nights, and if you have a dark area away from direct lighting, you’ll see the Milky Way shining brightly.
Galaxy NGC 6744 in Pavo - Wed 2nd Jul 2025
Published 2nd Jul 2025
This is NGC 6744, a spiral galaxy bearing similarities to our home galaxy, the Milky Way.
Starwatch for June 2025 - Mon 2nd Jun 2025
Published 2nd Jun 2025
The winter Milky Way shines across the sky from east to west in a blaze of starlight.
Eta Carinae Nebula (NGC 3372) - Sun 1st Jun 2025
Published 1st Jun 2025
Eta Carinae Nebula (NGC 3372) Distance: 7500 Light Years
Starwatch for May 2025 - Wed 30th Apr 2025
Published 30th Apr 2025
We have recently seen the destructive power of extreme weather events, such as cyclones and the flooding in southwest Queensland. It left in its wake flooded businesses, broken roads, power outages, and other problems. The repair bill will run into billions of dollars.
NGC 5139 - Omega Centauri - Tue 29th Apr 2025
Published 29th Apr 2025
Globular Cluster in Centaurus
Starwatch for April 2025 - Wed 2nd Apr 2025
Published 2nd Apr 2025
The crisp autumn evenings of April offer an ideal opportunity to explore the majesty of the southern sky. Go find yourself a nice dark spot in the back-garden, and let your eyes become accustomed to the darkness. Notice how many more stars you can see, even after a few minutes, as the pupils of your eyes expand to let as much light in as possible.
IC434 -The Horsehead Nebula - Tue 1st Apr 2025
Published 1st Apr 2025
Distance: 1500 Light Years |Constellation - Orion
Starwatch - March 2025 - Mon 3rd Mar 2025
Published 3rd Mar 2025
There's nothing more magical than to lie down on your back lawn on a warm summer evening and gaze up at the brilliant night sky.
Eta Carinae Nebula (NGC 3372) - Sat 1st Mar 2025
Published 1st Mar 2025
Distance: 7500 Light Years
Starwatch - February 2025 - Wed 5th Feb 2025
Published 5th Feb 2025
Two bright beacons hold centre stage in our night sky during February. In the beautiful pastel hues of an Australian summer sunset.
M104 - The Sombrero Galaxy - Tue 4th Feb 2025
Published 4th Feb 2025
Distance: 31 Million Light Years
Starwatch - January 2025 - Wed 1st Jan 2025
Published 1st Jan 2025
There's nothing more magical than to lie down on your back lawn on a warm summer evening and gaze up at the brilliant night sky.
The Pleiades star cluster - Tue 31st Dec 2024
Published 31st Dec 2024
The Pleiades star cluster (The Seven Sisters) Distance: 435 Light Years
Starwatch - December 2024 - Sun 1st Dec 2024
Published 1st Dec 2024
The stars that shine at night do so from immense distances.
Starwatch - November 2024 - Mon 4th Nov 2024
Published 4th Nov 2024
We recently saw the destructive power of hurricanes Milton and Helene, as they cut a path of destruction through various states in the US. They left in their wake flooded businesses, broken roads, power outages, and other problems. The repair bill will run into billions of dollars.
Large Magellanic Cloud - Fri 1st Nov 2024
Published 1st Nov 2024
Distance: 163,000 light years Right Ascension 05 : 23.6 Declination -69 : 45
Starwatch - October 2024 - Mon 30th Sep 2024
Published 30th Sep 2024
After a spectacular encounter with Pluto back in July 2015, the New Horizons spacecraft was redirected to visit a more distant object, known as 2014 MU69.
OCTOBER’S DEEP SKY HIGHLIGHT - Sun 29th Sep 2024
Published 29th Sep 2024
M31—The Andromeda Galaxy Distance: 2.5 million Light Years
Starwatch - September 2024 - Sat 31st Aug 2024
Published 31st Aug 2024
Spring is just around the corner, and with it, comes the promise of warmer evenings and clearer skies. And hopefully the opportunity to spend more time looking up!
NGC 253 – Galaxy in Sculptor - Fri 30th Aug 2024
Published 30th Aug 2024
NGC 253 is the brightest member of the Sculptor Group of galaxies.
Starwatch - August 2024 - Tue 30th Jul 2024
Published 30th Jul 2024
f you're brave enough to venture outside these cold winter nights, you'll be greeted by the heart of our Milky Way galaxy directly overhead. Find yourself a dark space in your backyard on a clear moonless night, and look straight up.
The Swan Nebula - Mon 29th Jul 2024
Published 29th Jul 2024
M17 – The Swan Nebula in Sagittarius
Starwatch July 2024 - Mon 8th Jul 2024
Published 8th Jul 2024
Look up overhead on any of these frosty winter’s nights, and as long as you have a dark area away from direct lighting, you’ll see the band of the Milky Way shining brightly.
Merging Galaxies - Sun 7th Jul 2024
Published 7th Jul 2024
NGC 4038-4039 Merging Galaxies - The Antennae. Distance: 45 million Light Years.
Starwatch June 2024 - Sun 2nd Jun 2024
Published 2nd Jun 2024
About half-way up the northern evening sky, a bright star shines.
The Trifid Nebula - Sat 1st Jun 2024
Published 1st Jun 2024
M20 – The Trifid Nebula in Sagittarius
Starwatch May 2024 - Thu 2nd May 2024
Published 2nd May 2024
A myriad of bright stars adorn the late autumn evening sky.
Galaxy NGC 5128 - Wed 1st May 2024
Published 1st May 2024
Galaxy NGC 5128—Centaurus A
Comet Pons-Brooks - Wed 10th Apr 2024
Published 10th Apr 2024
Looking west on the evening of April 27., 30 minutes after sunset. Locate the orange star Aldebaran, then scan to the left until you come to a fuzzy spot in the sky. Train your binoculars on it, the comet will be 239 million kilometres away. Graphic generated with Stellarium planetarium software.
M104 - The Sombrero Galaxy - Tue 9th Apr 2024
Published 9th Apr 2024
M104 - The Sombrero Galaxy. Distance: 31 Million Light Years
Starwatch - April 2024 - Mon 8th Apr 2024
Published 9th Apr 2024
Some of the brightest stars in the whole sky can be seen during these crisp autumn evenings.
Starwatch - March 2024 - Wed 6th Mar 2024
Published 6th Mar 2024
What a wonderful time of the year this is to be observing the night sky. The weather is warm, the nights clear, and the Milky Way shines directly overhead!
Object of the Month - Mon 4th Mar 2024
Published 4th Mar 2024
Eta Carinae Nebula (NGC 3372)
Distance: 7500 Light Years
Right Ascension: 10 : 43.8 | Declination: -59 : 52
Some of the brightest stars in the whole sky can be seen during these crisp autumn evenings.
As red Betelgeuse and blue Rigel set with Orion, the Hunter in the west; fiery red Antares rises in the east.
For me, I don't think there are any other constellations in the sky that herald the coming of the seasons so
well as these two do. Orion in the east, signals summer is around the corner, whilst Scorpius in the east, brings the chill winds of winter with it.
Over in the northeast another star shines. This is Arcturus, in the constellation Bootes, the herdsman. It's an orange-giant star, and it's unusually old as naked-eye stars go: about 10 billion years — roughly twice the age of the Sun, Earth, and solar system. Arcturus may thus be the oldest object you've ever seen.
Arcturus is the third-brightest star in Earth's night sky. It appears so bright for a couple of reasons. First, Arcturus really is a bright star; it produces more visible light than most stars. If
you placed Arcturus side by side with our own star, the Sun, it would appear more than a hundred times brighter. And second, Arcturus is fairly close to us, at a distance of just 37 lightyears.
This nearness has another effect on how we see Arcturus: It moves across the sky faster than almost any other star. All
stars are in constant motion as they orbit the centre of our Milky Way galaxy. But they're so far away that their motion is imperceptible on human timescales. Astronomers must use sensitive instruments to measure this motion.
Arcturus is moving toward the constellation Virgo, which is higher in the sky above Arcturus, at about half a degree every millennium — a distance equal to the width of the full Moon.
Arcturus will move out of Bootes and into Virgo in about 20,000 years.